-
 Red Ocean vs Blue Ocean Strategy
Red Ocean vs Blue Ocean Strategy
-
 Value Innovation
Value Innovation
-
 Strategy Canvas
Strategy Canvas
-
 Buyer Utility Map
Buyer Utility Map
-
 Three Tiers of Noncustomers
Three Tiers of Noncustomers
-
 Six Paths Framework
Six Paths Framework
-
 Four Actions Framework
Four Actions Framework
-
 ERRC Grid
ERRC Grid
-
 Pioneer Migrator Settler Map
Pioneer Migrator Settler Map
-
 Price Corridor of the Mass
Price Corridor of the Mass
-
 Sequence of Creating a Blue Ocean
Sequence of Creating a Blue Ocean
-
 Five Steps to a Blue Ocean Shift
Five Steps to a Blue Ocean Shift
-
 Three Components of Blue Ocean Shift
Three Components of Blue Ocean Shift
-
 Three Components of Humanness
Three Components of Humanness
-
 Four Hurdles to Strategy Execution
Four Hurdles to Strategy Execution
-
 Fair Process
Fair Process
-
 Tipping Point Leadership
Tipping Point Leadership
-
 Blue Ocean Vs Conventional Leadership
Blue Ocean Vs Conventional Leadership
-
 Leadership Canvas
Leadership Canvas
-
 Blue Ocean Leadership Grid
Blue Ocean Leadership Grid
-
 Four-Step Blue Ocean Leadership Process
Four-Step Blue Ocean Leadership Process
-
 Cost of Disengaged Employees
Cost of Disengaged Employees
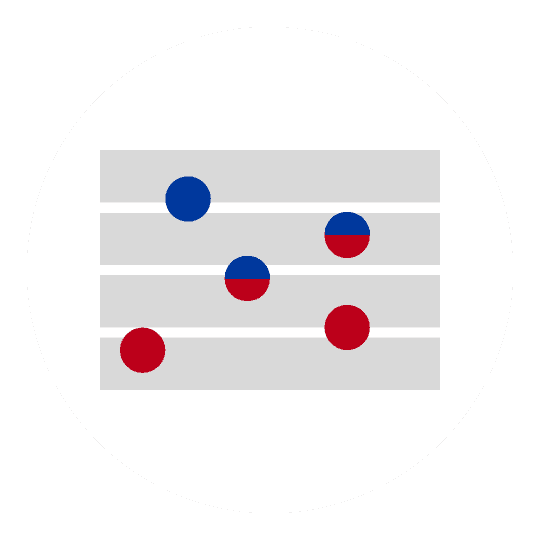
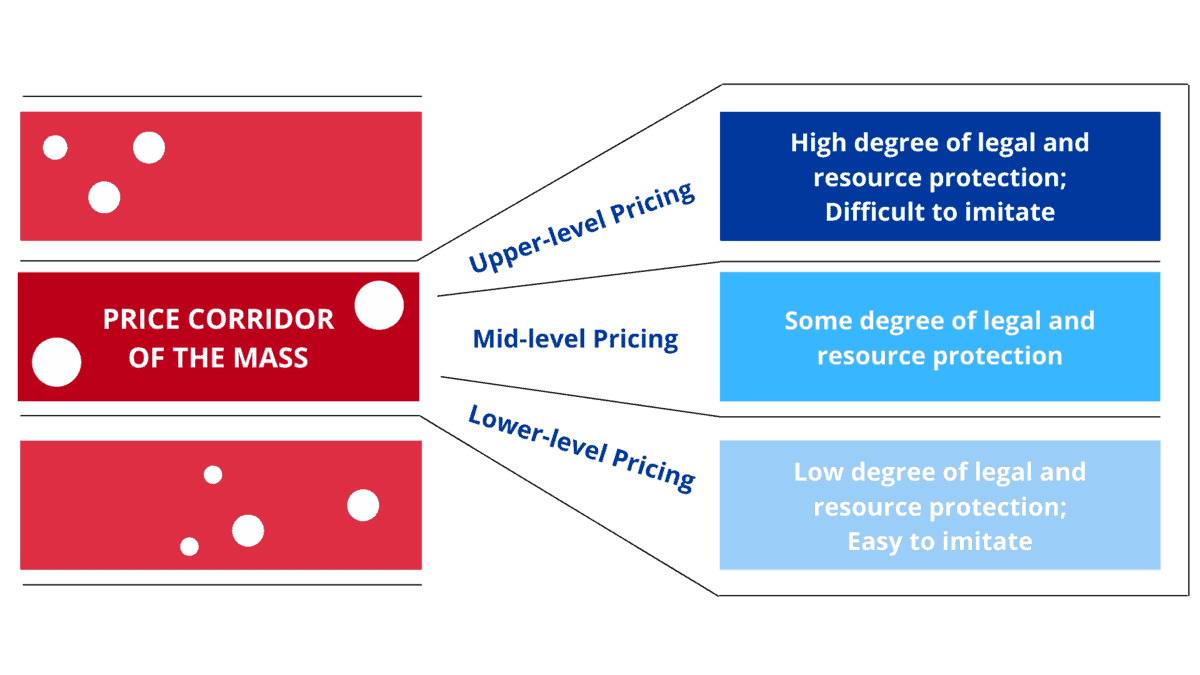
PRICE CORRIDOR OF THE MASS
The Price Corridor of the Target Mass developed by Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne is a tool managers can use to determine the right price to unlock the mass of target buyers. When setting a strategic price for a product or service, managers must evaluate the trade-offs that buyers consider when making their purchasing decision, as well as the level of legal and resource protection that will block other companies from imitating their offering.
Step one:
Identify the price corridor of the mass.
Step two:
Specify a price level within the price corridor.
Three alternative product service types:
- Same Form
- Different Form, Same Function
- Different Form and Function, Same Objective
Size of circle is proportional to number
of buyers that product/service attracts
© Chan Kim & Renée Mauborgne. All rights reserved.
To set the strategic price, first identify the price corridor of the target mass, that is, the price range that attracts the mass of target buyers. Key to determining the strategic price is for managers to understand the price sensitivities of buyers who will be comparing the new offering with a host of very different-looking products and services offered outside the group of traditional competitors. For example, buyers can choose between several movie theatres, but they can also decide to go to restaurants and bars. Managers should consider two categories of products/services that are beyond an industry’s boundaries in identifying the price corridor of the mass: products and services that take different forms but perform the same function, and products and services that have different forms and functions but serve the same objective.
Next, determine how high or low the strategic price should be set within the corridor without inviting imitation from the competition.
A company must consider two sets of factors: the level of legal and resource protection the new offering has to block imitation, and secondly the degree to which the company owns some exclusive asset or core capability that can also block imitation.
The higher the level of protection against imitation, the higher the strategic price can be within the price range that still attracts the mass of target buyers. For example, if the product or service has strong patents and hard-to-imitate service capabilities one can use upper-boundary strategic pricing to attract the mass of buyers. On the other hand, if a manager is uncertain about their patent and asset protection they should consider pricing somewhere in the middle to lower end of the corridor.
-
 Red Ocean vs Blue Ocean Strategy
Red Ocean vs Blue Ocean Strategy
-
 Value Innovation
Value Innovation
-
 Strategy Canvas
Strategy Canvas
-
 Buyer Utility Map
Buyer Utility Map
-
 Three Tiers of Noncustomers
Three Tiers of Noncustomers
-
 Six Paths Framework
Six Paths Framework
-
 Four Actions Framework
Four Actions Framework
-
 ERRC Grid
ERRC Grid
-
 Pioneer Migrator Settle Map
Pioneer Migrator Settle Map
-
 Price Corridor of the Mass
Price Corridor of the Mass
-
 Sequence of Creating a Blue Ocean
Sequence of Creating a Blue Ocean
-
 Five Steps to a Blue Ocean Shift
Five Steps to a Blue Ocean Shift
-
 Three Components of Blue Ocean Shift
Three Components of Blue Ocean Shift
-
 Three Components of Humanness
Three Components of Humanness
-
 Four Hurdles to Strategy Execution
Four Hurdles to Strategy Execution
-
 Fair Process
Fair Process
-
 Tipping Point Leadership
Tipping Point Leadership
-
 Blue Ocean Vs Conventional Leadership
Blue Ocean Vs Conventional Leadership
-
 Leadership Canvas
Leadership Canvas
-
 Blue Ocean Leadership Grid
Blue Ocean Leadership Grid
-
 Four-Step Blue Ocean Leadership Process
Four-Step Blue Ocean Leadership Process
-
 Cost of Disengaged Employees
Cost of Disengaged Employees

BLUE OCEAN SPRINT
Learn how to leave the competition behind. Discover how to create a new market space while lowering your costs, fast.
“LOVED this course. No nonsense, 100% practical tools I can start implementing TODAY in my organisation!” Amalia C., Google
Join thousands of leaders like you who are creating innovative companies, products, and services that stand out from the crowd.
THE BLUE OCEAN STRATEGY PRACTITIONER PROGRAM

Transform your strategic perspective, master blue ocean tools and frameworks, & learn to unlock new growth opportunities
Get started with new market creation with our live, interactive, expert-led program.